Track an experiment while training a Pytorch model with a SageMaker Training Job
This notebook’s CI test result for us-west-2 is as follows. CI test results in other regions can be found at the end of the notebook.
This notebook shows how you can use the SageMaker SDK to track a Machine Learning experiment using a Pytorch model trained in a SageMaker Training Job with Script mode, where you will provide the model script file.
We introduce two concepts in this notebook -
Experiment: An experiment is a collection of runs. When you initialize a run in your training loop, you include the name of the experiment that the run belongs to. Experiment names must be unique within your AWS account.
Run: A run consists of all the inputs, parameters, configurations, and results for one iteration of model training. Initialize an experiment run for tracking a training job with Run().
To execute this notebook in SageMaker Studio, you should select the PyTorch 1.12 Python 3.8 CPU Optimizer image.
You can track artifacts for experiments, including datasets, algorithms, hyperparameters and metrics. Experiments executed on SageMaker such as SageMaker training jobs are automatically tracked and any existen SageMaker experiment on your AWS account is automatically migrated to the new UI version.
In this notebook we will demonstrate the capabilities through an MNIST handwritten digits classification example. The notebook is organized as follow:
Train a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) Model and log the model training metrics
Tune the hyperparameters that configures the number of hidden channels and the optimized in the model. Track teh parameter’s configuration, resulting model loss and accuracy and automatically plot a confusion matrix using the Experiments capabilities of the SageMaker SDK.
Analyse your model results and plot graphs comparing your model different runs generated from the tunning step 3.
Runtime
This notebook takes approximately 45 minutes to run.
Contents
Install modules
Let’s ensure we have the latest SageMaker SDK available, including the SageMaker Experiments functionality
[ ]:
import sys
[ ]:
# update boto3 and sagemaker to ensure latest SDK version
!{sys.executable} -m pip install --upgrade pip
!{sys.executable} -m pip install --upgrade boto3
!{sys.executable} -m pip install --upgrade sagemaker
!{sys.executable} -m pip install torch
!{sys.executable} -m pip install torchvision
Setup
Import required libraries and set logging and experiment configuration
SageMaker Experiments now provides the Run class that allows you to create a new experiment run.
[ ]:
from sagemaker.pytorch import PyTorch
from sagemaker.experiments.run import Run
from sagemaker.session import Session
from sagemaker import get_execution_role
from sagemaker.utils import unique_name_from_base
role = get_execution_role()
region = Session().boto_session.region_name
# set new experiment configuration
experiment_name = unique_name_from_base("training-job-experiment")
run_name = "experiment-run-example"
print(experiment_name)
Create model training script
Let’s create mnist.py, the pytorch script file to train our model.
[ ]:
!mkdir -p script
[ ]:
%%writefile ./script/mnist.py
# ensure that the latest version of the SageMaker SDK is available
import os
os.system("pip install -U sagemaker")
import argparse
import json
import logging
import sys
import time
from os.path import join
import boto3
import torch
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from sagemaker.session import Session
from sagemaker.experiments.run import load_run
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
logger.addHandler(logging.StreamHandler(sys.stdout))
if "SAGEMAKER_METRICS_DIRECTORY" in os.environ:
log_file_handler = logging.FileHandler(
join(os.environ["SAGEMAKER_METRICS_DIRECTORY"], "metrics.json")
)
formatter = logging.Formatter(
"{'time':'%(asctime)s', 'name': '%(name)s', \
'level': '%(levelname)s', 'message': '%(message)s'}",
style="%",
)
log_file_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
logger.addHandler(log_file_handler)
# Based on https://github.com/pytorch/examples/blob/master/mnist/main.py
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_channels, kernel_size, drop_out):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, hidden_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(hidden_channels, 20, kernel_size=kernel_size)
self.conv2_drop = torch.nn.Dropout2d(p=drop_out)
self.fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(320, 50)
self.fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(50, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.nn.functional.relu(torch.nn.functional.max_pool2d(self.conv1(x), 2))
x = torch.nn.functional.relu(
torch.nn.functional.max_pool2d(self.conv2_drop(self.conv2(x)), 2)
)
x = x.view(-1, 320)
x = torch.nn.functional.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = torch.nn.functional.dropout(x, training=self.training)
x = self.fc2(x)
return torch.nn.functional.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
def log_performance(model, data_loader, device, epoch, run, metric_type="Test"):
model.eval()
loss = 0
correct = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data, target in data_loader:
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
output = model(data)
loss += torch.nn.functional.nll_loss(
output, target, reduction="sum"
).item() # sum up batch loss
# get the index of the max log-probability
pred = output.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
loss /= len(data_loader.dataset)
accuracy = 100.0 * correct / len(data_loader.dataset)
# log metrics
run.log_metric(name=metric_type + ":loss", value=loss, step=epoch)
run.log_metric(name=metric_type + ":accuracy", value=accuracy, step=epoch)
logger.info(
"{} Average loss: {:.4f}, {} Accuracy: {:.4f}%;\n".format(
metric_type, loss, metric_type, accuracy
)
)
def train_model(
run, train_set, test_set, data_dir="mnist_data", optimizer="sgd", epochs=10, hidden_channels=10
):
"""
Function that trains the CNN classifier to identify the MNIST digits.
Args:
run (sagemaker.experiments.run.Run): SageMaker Experiment run object
train_set (torchvision.datasets.mnist.MNIST): train dataset
test_set (torchvision.datasets.mnist.MNIST): test dataset
data_dir (str): local directory where the MNIST datasource is stored
optimizer (str): the optimization algorthm to use for training your CNN
available options are sgd and adam
epochs (int): number of complete pass of the training dataset through the algorithm
hidden_channels (int): number of hidden channels in your model
"""
# log the parameters of your model
run.log_parameter("device", "cpu")
run.log_parameters(
{
"data_dir": data_dir,
"optimizer": optimizer,
"epochs": epochs,
"hidden_channels": hidden_channels,
}
)
# train the model on the CPU (no GPU)
device = torch.device("cpu")
# set the seed for generating random numbers
torch.manual_seed(42)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_set, batch_size=1000, shuffle=True)
logger.info(
"Processes {}/{} ({:.0f}%) of train data".format(
len(train_loader.sampler),
len(train_loader.dataset),
100.0 * len(train_loader.sampler) / len(train_loader.dataset),
)
)
logger.info(
"Processes {}/{} ({:.0f}%) of test data".format(
len(test_loader.sampler),
len(test_loader.dataset),
100.0 * len(test_loader.sampler) / len(test_loader.dataset),
)
)
model = Net(hidden_channels, kernel_size=5, drop_out=0.5).to(device)
model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model)
momentum = 0.5
lr = 0.01
log_interval = 100
if optimizer == "sgd":
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=lr, momentum=momentum)
else:
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
for epoch in range(1, epochs + 1):
print("Training Epoch:", epoch)
model.train()
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader, 1):
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(data)
loss = torch.nn.functional.nll_loss(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch_idx % log_interval == 0:
logger.info(
"Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)], Train Loss: {:.6f};".format(
epoch,
batch_idx * len(data),
len(train_loader.sampler),
100.0 * batch_idx / len(train_loader),
loss.item(),
)
)
log_performance(model, train_loader, device, epoch, run, "Train")
log_performance(model, test_loader, device, epoch, run, "Test")
# log confusion matrix
with torch.no_grad():
for data, target in test_loader:
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
output = model(data)
pred = output.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
run.log_confusion_matrix(target, pred, "Confusion-Matrix-Test-Data")
return model
def model_fn(model_dir):
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
hidden_channels = int(os.environ.get("hidden_channels", "5"))
kernel_size = int(os.environ.get("kernel_size", "5"))
dropout = float(os.environ.get("dropout", "0.5"))
model = torch.nn.DataParallel(Net(hidden_channels, kernel_size, dropout))
with open(os.path.join(model_dir, "model.pth"), "rb") as f:
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(f))
return model.to(device)
def save_model(model, model_dir, run):
logger.info("Saving the model.")
path = os.path.join(model_dir, "model.pth")
# recommended way from http://pytorch.org/docs/master/notes/serialization.html
torch.save(model.cpu().state_dict(), path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
"--epochs",
type=int,
default=10,
metavar="N",
help="number of epochs to train (default: 10)",
)
parser.add_argument("--optimizer", type=str, default="sgd", help="optimizer for training.")
parser.add_argument(
"--hidden_channels",
type=int,
default=10,
help="number of channels in hidden conv layer",
)
parser.add_argument("--region", type=str, default="us-east-2", help="SageMaker Region")
# Container environment
parser.add_argument("--hosts", type=list, default=json.loads(os.environ["SM_HOSTS"]))
parser.add_argument("--current-host", type=str, default=os.environ["SM_CURRENT_HOST"])
parser.add_argument("--model-dir", type=str, default=os.environ["SM_MODEL_DIR"])
parser.add_argument("--num-gpus", type=int, default=os.environ["SM_NUM_GPUS"])
args = parser.parse_args()
# download the dataset
# this will not only download data to ./mnist folder, but also load and transform (normalize) them
datasets.MNIST.urls = [
f"https://sagemaker-example-files-prod-{args.region}.s3.amazonaws.com/datasets/image/MNIST/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz",
f"https://sagemaker-example-files-prod-{args.region}s.s3.amazonaws.com/datasets/image/MNIST/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz",
f"https://sagemaker-example-files-prod-{args.region}.s3.amazonaws.com/datasets/image/MNIST/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz",
f"https://sagemaker-example-files-prod-{args.region}.s3.amazonaws.com/datasets/image/MNIST/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz",
]
train_set = datasets.MNIST(
"mnist_data",
train=True,
transform=transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))]
),
download=True,
)
test_set = datasets.MNIST(
"mnist_data",
train=False,
transform=transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))]
),
download=True,
)
session = Session(boto3.session.Session(region_name=args.region))
with load_run(sagemaker_session=session) as run:
run.log_parameters(
{"num_train_samples": len(train_set.data), "num_test_samples": len(test_set.data)}
)
for f in os.listdir(train_set.raw_folder):
print("Logging", train_set.raw_folder + "/" + f)
run.log_file(train_set.raw_folder + "/" + f, name=f, is_output=False)
model = train_model(
run,
train_set,
test_set,
data_dir="mnist_data",
optimizer=args.optimizer,
epochs=args.epochs,
hidden_channels=args.hidden_channels,
)
save_model(model, args.model_dir, run)
The cell above saves the mnist.py file to our script folder. The file implements the code necessary to train our PyTorch model in SageMaker, using the SageMaker PyTorch image. It uses the load_run function to automatically detect the experiment configuration and run.log_parameter, run.log_parameters, run.log_file, run.log_metric and run.log_confusion_matrix to track the model training
Train model with Run context
Let’s now train the model with passing the experiement run context to the training job
[ ]:
%%time
# Start training job with experiment setting
with Run(experiment_name=experiment_name, run_name=run_name, sagemaker_session=Session()) as run:
est = PyTorch(
entry_point="./script/mnist.py",
role=role,
model_dir=False,
framework_version="1.12",
py_version="py38",
instance_type="ml.c5.xlarge",
instance_count=1,
hyperparameters={"epochs": 10, "hidden_channels": 5, "optimizer": "adam", "region": region},
keep_alive_period_in_seconds=3600,
)
est.fit()
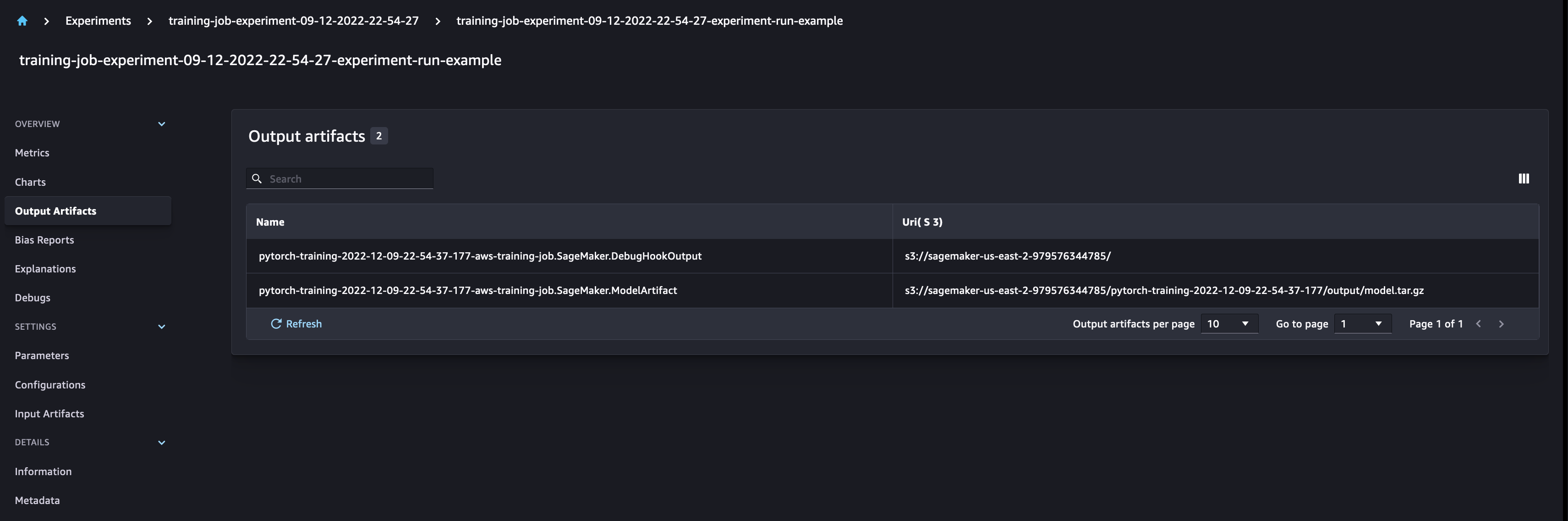
Checking the SageMaker Experiments UI, you can observe the Experiment run, populated with the metrics and parameters logged. We can also see the automatically generated outputs for the model data
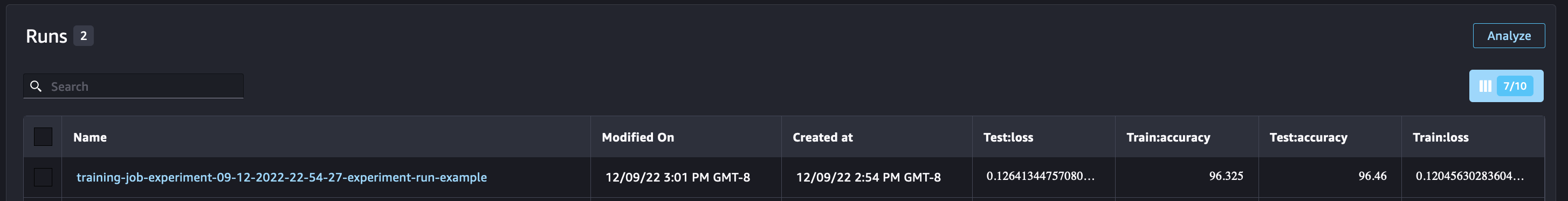
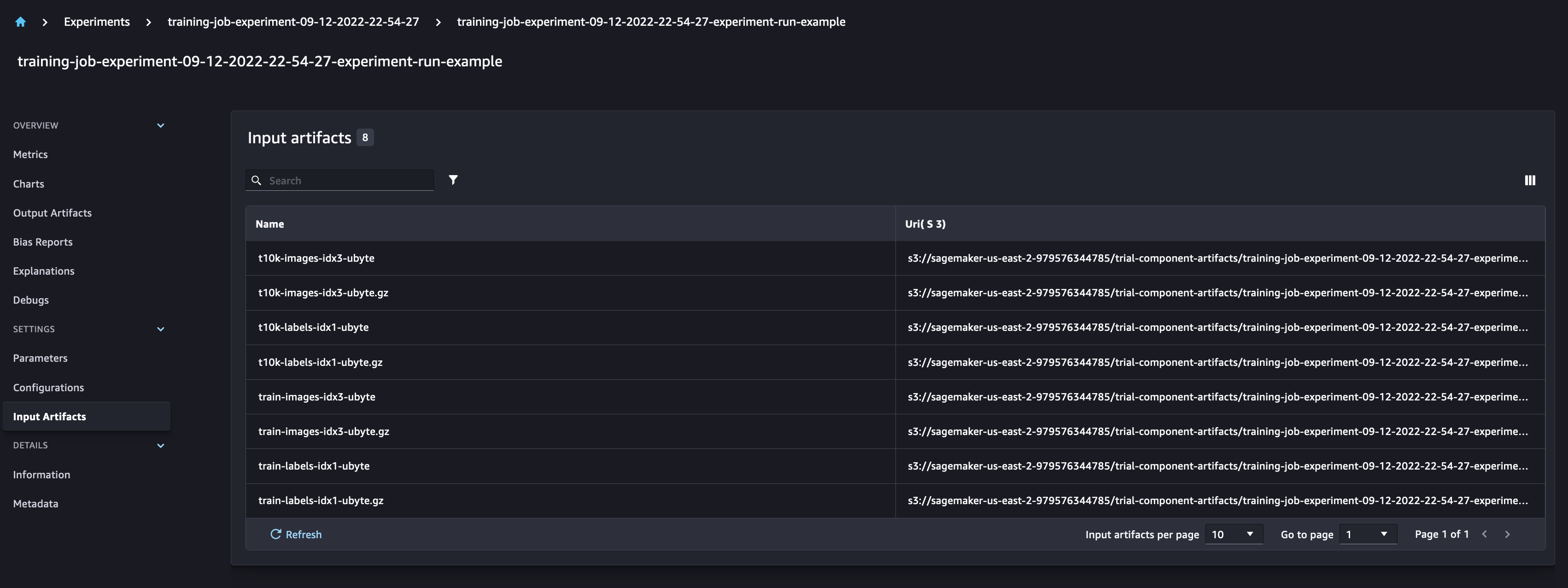
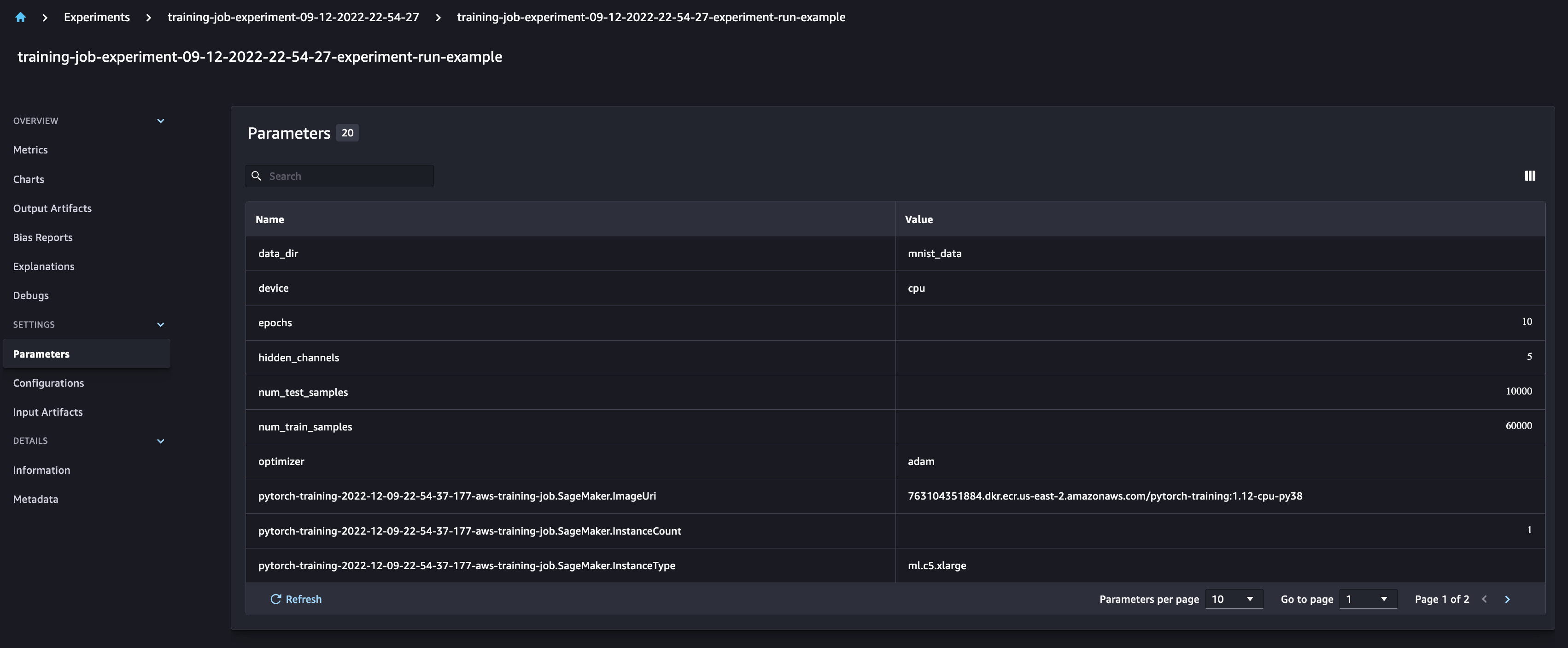
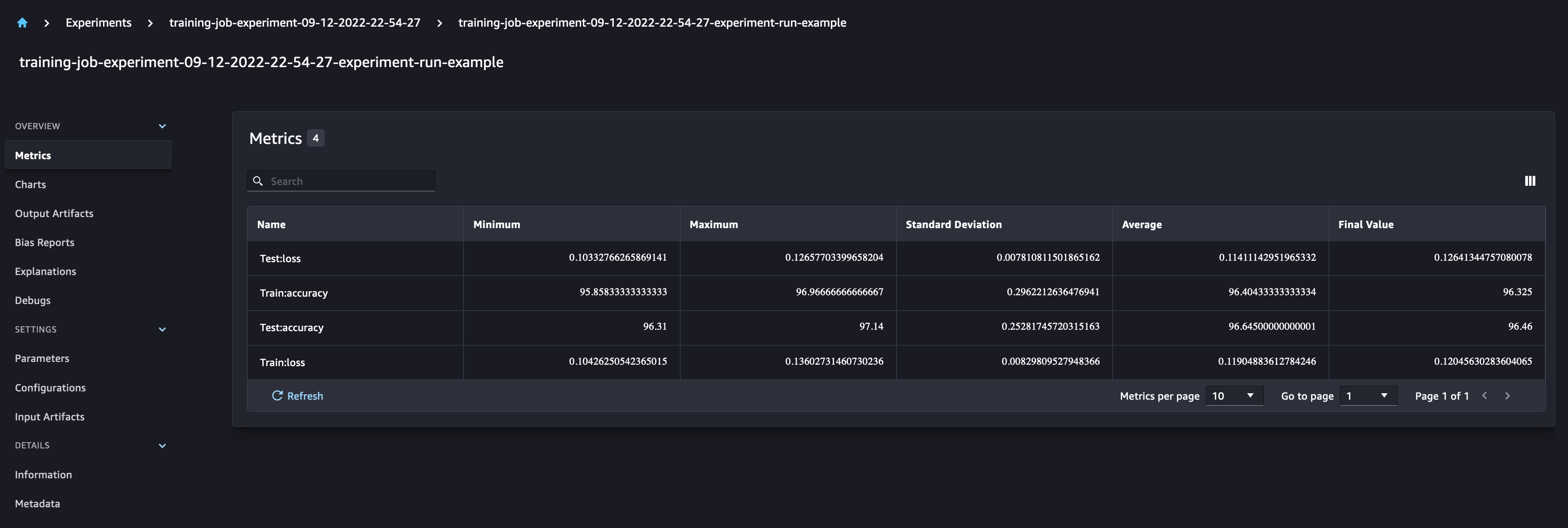
Notebook CI Test Results
This notebook was tested in multiple regions. The test results are as follows, except for us-west-2 which is shown at the top of the notebook.